康托展开
定义
康托展开是一个全排列到一个自然数的双射,常用于构建哈希表时的空间压缩。 康托展开的实质是计算当前排列在所有由小到大全排列中的顺序,因此是可逆的。
公式
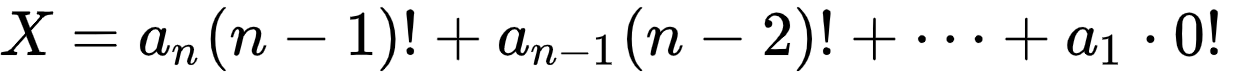
其中 ai 为整数,且 0 ≤ ai ≤ i, 1 ≤ i ≤ n .
解释
以 [4, 2, 3, 1] 为例,以 4 为第一位的排列之前的排列的第一位可能为 1、2、3,共 3 种情况,而第 2、3、4 位上的顺序又有 3! 种可能。此时 an = 3,n - 1 = 3, 故第一位为 4 的排列之前共有 18 种排列。以此类推,可计算在第一位为 4,第二位为 2 的情况之前的排列数量,此时比 2 小的只有一个数 1,故 an = 1, n - 2 = 2,故第二项为 2。后续过程类似,由于计算的是当前排列的次序,故还需将结果加 1。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class CantorExpansion {
final int[] facts = {1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880};
public int getFactorial(int n) {
if (n < 10) return facts[n];
return n * getFactorial(n - 1);
}
public int cantor(int[] nums) {
int result = 0;
int arrLen = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < arrLen; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arrLen; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) cnt++;
}
result += cnt * getFactorial(arrLen - i - 1);
}
return result + 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int nums[] = {4, 2, 3, 1};
System.out.println(new CantorExpansion().cantor(nums));
}
}
|
逆康托展开
因为排列的次序与排列是一一对应的,故可由排列数直接推得排列。
例如,对数组 [1, 2, 3, 4] 的全排列序列来说,求第 23 个排列:
- 首先减去 1 求得该序列前共有 22 种排列
- 再用 22 除 (4 - 1)!,商 3 余 4,故这个排列比第一位小的共有 3 个数,故第一位为 4
- 用 4 除 (3 - 1)!,商 2 余 0,故剩余的数中比第二位小的数共有 2 个,所以第二位为 3
- 用 0 除 (2 - 1)!,商 0 余 0,故剩余的数中比第三位小的数有 0 个,所以第三位为 1
- 用 0 除 (1 - 1)!,商 0 余 0,故比第四位小的数有 0 个,所以第四位为仅剩的 2
所以第 23 个排列为 4312。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| class CantorExpansion {
final int[] facts = {1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880};
public int getFactorial(int n) {
if (n < 10) return facts[n];
return n * getFactorial(n - 1);
}
public String inverseCantor(int[] nums, int n) {
int arrLen = nums.length;
char[] result = new char[arrLen];
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[arrLen];
n--;
for (int i = 0; i < arrLen; i++) {
int tmpFact = getFactorial(arrLen - 1 - i);
int cnt = n / tmpFact;
n %= tmpFact;
for (int j = 0; j < arrLen; j++) {
if (isVisited[j]) continue;
if (cnt-- == 0) {
isVisited[j] = true;
result[i] = (char) (nums[j] + '0');
break;
}
}
}
return String.valueOf(result);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int nums[] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
System.out.println(new CantorExpansion().inverseCantor(nums, 23));
}
}
|
第 k 个排列
给出集合 [1,2,3,…,n],其所有元素共有 n! 种排列。
按大小顺序列出所有排列情况,并一一标记,当 n = 3 时, 所有排列如下:
- “123”
- “132”
- “213”
- “231”
- “312”
- “321”
给定 n 和 k,返回第 k 个排列。
说明:
- 给定 n 的范围是 [1, 9]。
- 给定 k 的范围是[1, n!]。
示例 1:
输入: n = 3, k = 3
输出: “213”
示例 2:
输入: n = 4, k = 9
输出: “2314”
题解
采用逆康托展开直接计算
Java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| class Solution {
final int[] facts = {1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880};
public int getFactorial(int n) {
if (n < 10) return facts[n];
return n * getFactorial(n - 1);
}
public String getPermutation(int n, int k) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[n];
k--;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int tmpFact = getFactorial(n - 1 - i);
int cnt = k / tmpFact;
k %= tmpFact;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (isVisited[j]) continue;
if (cnt-- == 0) {
isVisited[j] = true;
result.append(j + 1);
break;
}
}
}
return String.valueOf(result);
}
}
|
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.facts = [1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880]
def get_fact(self, n: int) -> int:
if n < 10: return self.facts[n]
return n * self.get_fact(n - 1)
def getPermutation(self, n: int, k: int) -> str:
result = []
is_visited = [False] * n
k -= 1
for i in range(n):
tmp_fact = self.get_fact(n - 1 - i)
cnt = k // tmp_fact
k %= tmp_fact
for j in range(n):
if is_visited[j]: continue
if cnt == 0:
is_visited[j] = True
result.append(str(j + 1))
break
cnt -= 1
return ''.join(result)
|
Go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| import (
"strconv"
"strings"
)
var facts = []int{1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880}
func getFact(n int) int {
if n < 10 {
return facts[n]
}
return n * getFact(n-1)
}
func getPermutation(n int, k int) string {
var result []string
isVisited := make([]bool, n)
k--
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
tmpFact := getFact(n - 1 - i)
cnt := k / tmpFact
k %= tmpFact
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if isVisited[j] {
continue
}
if cnt == 0 {
isVisited[j] = true
result = append(result, strconv.Itoa(j+1))
break
}
cnt--
}
}
return strings.Join(result, "")
}
|