给定一个无重复元素 的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [2, 3, 6, 7], target = 7,
所求解集为:
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 30
1 <= candidates[i] <= 200
candidate 中的每个元素都是独一无二的。
1 <= target <= 500
题解 参考题解
思路分析 回溯法 (探索与回溯法)是一种选优搜索法,又称为试探法,按选优条件向前搜索,以达到目标。但当探索到某一步时,发现原先选择并不优或达不到目标,就退回一步重新选择,这种走不通就退回再走的技术为回溯法,而满足回溯条件的某个状态的点称为“回溯点”。
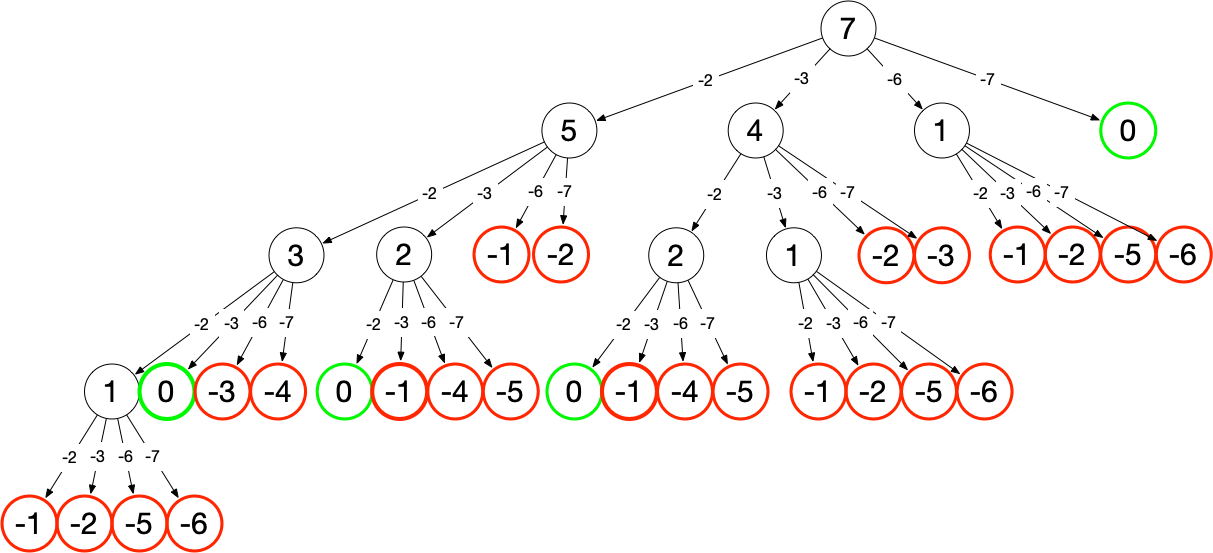
本题为回溯法经典例题,以 candidates = [2, 3, 6, 7] , target = 7 为例,可用 target 减去 candidates 中的元素,得到新的 target ,再减去 candidates 中的元素,多次相减,若在某次迭代中 target 变为 0,则减数的集合即为一个解;若 target 小于 0 则回退至上一步继续寻找下一个解。如下图所示,其中绿色叶节点所在的路径即为一解。
以上算法实现如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import java.util.*;class Solution { List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { int arrLen = candidates.length; if (arrLen == 0 ) return results; Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); dfs(candidates, 0 , arrLen, target, path); return results; } public void dfs (int [] candidates, int begin, int arrLen, int target, Deque<Integer> path) { if (target < 0 ) return ; if (target == 0 ) { results.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < arrLen; i++) { path.addLast(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates, i, arrLen, target - candidates[i], path); path.removeLast(); } } }
输出:
1 2 3 4 [ 2 2 3 ] [ 2 3 2 ] [ 3 2 2 ] [ 7 ]
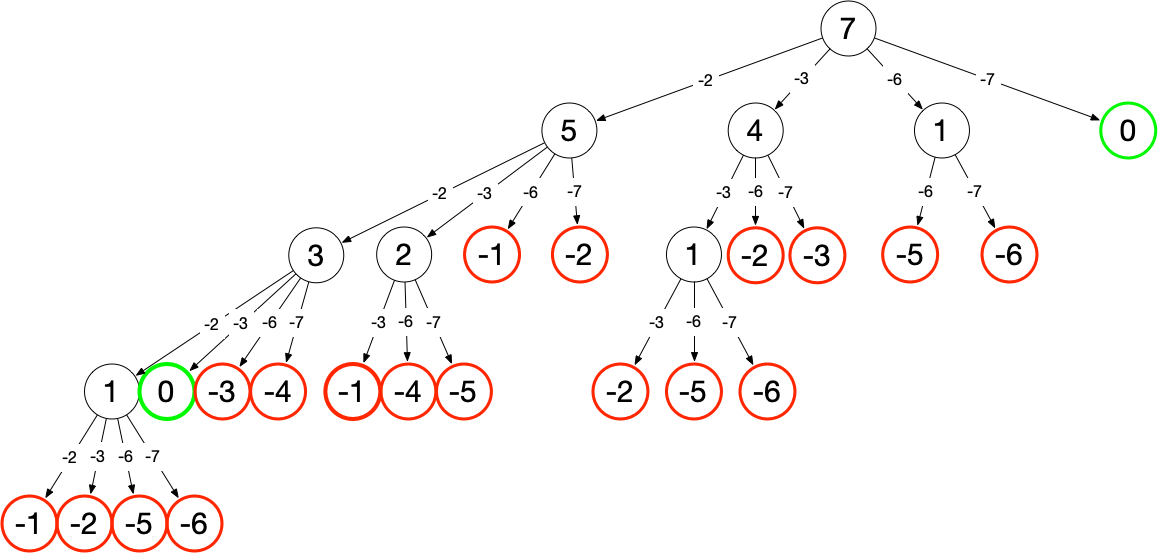
可以看到出现了重复解,这是由于每次计算下一层的 target 时均考虑了 candidates 的所有情况。若要避免这种重复,可在每个分支上排除之前已计算过的 candidates 值,如在 7 - 2 = 5 分支上已考虑了所有 candidates[i] = 2 的情况,在 7 - 3/6/7 三个分支上无需重复考虑。去重后树结构如下:
实现如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import java.util.*;class Solution { List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { int arrLen = candidates.length; if (arrLen == 0 ) return results; Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); dfs(candidates, 0 , arrLen, target, path); return results; } public void dfs (int [] candidates, int begin, int arrLen, int target, Deque<Integer> path) { if (target < 0 ) return ; if (target == 0 ) { results.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = begin; i < arrLen; i++) { path.addLast(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates, i, arrLen, target - candidates[i], path); path.removeLast(); } } }
此时输出即为无重复的解:
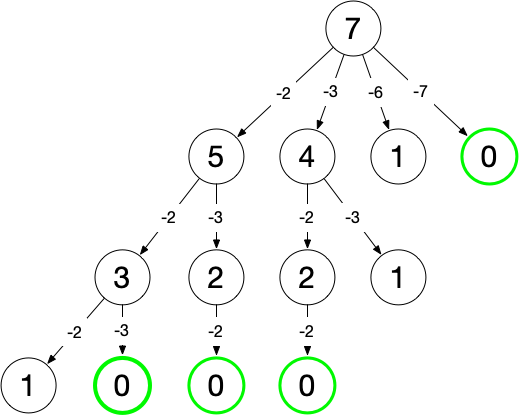
剪枝提速 在计算过程中,若 target 减去某个 candidates[i] 后小于 0,则大于该 candidates[i] 的值与 target 的差也必然小于 0。故可先对 candidates 数组进行升序排序,在遍历 candidates 数组的过程中,若 target < candidates[i] 则 i + 1 及其之后的位置也无需考虑。
注意: 采用这种剪枝方法必须先将 candidates 数组排序,否则若大于 target 的数排在前时,会提前触发 break,导致后边小于 target 的元素被跳过。
剪枝后的树如下,可以看到已减少了很多分支:
实现如下
Java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { int len = candidates.length; List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (len == 0 ) return result; Arrays.sort(candidates); Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); dfs(candidates, 0 , len, target, path, result); return result; } public void dfs (int [] candidates, int begin, int len, int target, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> result) { if (target == 0 ) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) { if (target < candidates[i]) break ; path.addLast(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates, i, len, target - candidates[i], path, result); path.removeLast(); } } }
Python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution : def __init__ (self ): self.path = [] self.results = [] def combinationSum (self, candidates: list , target: int ) -> list : arr_len = len (candidates) if arr_len == 0 : return self.results candidates.sort() self.dfs(candidates, 0 , arr_len, target) return self.results def dfs (self, candidates: list , begin: int , arr_len: int , target: int ) -> None : if target == 0 : self.results.append(self.path[:]) return for i in range (begin, arr_len): if (target - candidates[i] < 0 ): break self.path.append(candidates[i]) self.dfs(candidates, i, arr_len, target - candidates[i]) self.path.pop()
Go 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 func combinationSum (candidates []int , target int ) int { arrLen := len (candidates) var results [][]int if arrLen == 0 { return results } var path []int sort.Ints(candidates) dfs(candidates, 0 , arrLen, target, &results, path) return results } func dfs (candidates []int , begin, arrLen, target int , results *[][]int , path []int ) if target == 0 { *results = append (*results, path[:]) return } for i := begin; i < arrLen; i++ { if target - candidates[i] < 0 { break } path = append (path, candidates[i]) dfs(candidates, i, arrLen, target - candidates[i], results, path) path = path[:len (path)-1 ] } }
参考题解
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:
所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2, 5, 2, 1, 2], target = 5,
所求解集为:
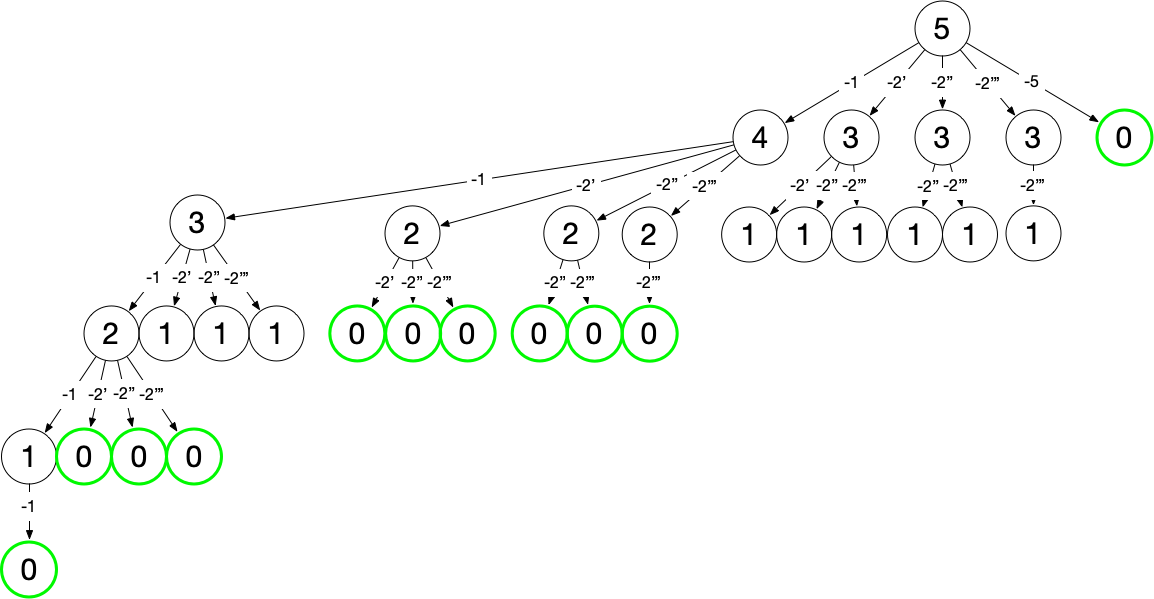
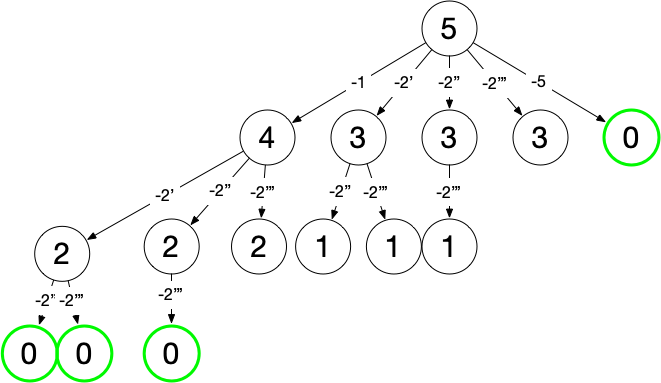
题解 以 candidates = [2, 5, 2, 1, 2] ,target = 5 为例,若采用 #39 题中的算法,得到以下树结构(以 2',2'',2''' 区分三个位置的 2):
输出如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [ 1 1 1 1 1 ] [ 1 1 1 2 ] [ 1 1 1 2 ] [ 1 1 1 2 ] [ 1 2 2 ] [ 1 2 2 ] [ 1 2 2 ] [ 1 2 2 ] [ 1 2 2 ] [ 1 2 2 ] [ 5 ]
需修改算法使之满足以下两个条件:
每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次
解集不能包含重复的组合
限制组合中数字的出现次数 在分支上遍历 candidates 时跳过已使用过的位置即可,此时树的结构如下:
实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { int len = candidates.length; List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (len == 0 ) return result; Arrays.sort(candidates); Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); dfs(candidates, 0 , len, target, path, result); return result; } public void dfs (int [] candidates, int begin, int len, int target, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> result) { if (target == 0 ) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) { if (target < candidates[i]) break ; path.addLast(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates, i + 1 , len, target - candidates[i], path, result); path.removeLast(); } } }
此时输出为:
1 2 3 4 [ 1 2 2 ] [ 1 2 2 ] [ 1 2 2 ] [ 5 ]
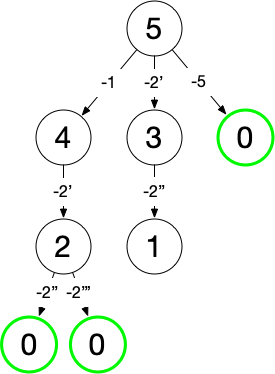
去除重复组合 从图中可知组合 [1, 2', 2''] 、[1, 2', 2'''] 和 [1, 2'', 2'''] 三者重复,要去除这种重复应跳过同一层级出现的相等元素。剪枝后的树结构如下:
最终输出为:
实现如下:
Java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) { int len = candidates.length; List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (len == 0 ) return result; Arrays.sort(candidates); Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque <>(); dfs(candidates, 0 , len, target, path, result); return result; } public void dfs (int [] candidates, int begin, int len, int target, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> result) { if (target == 0 ) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) { if (target < candidates[i]) break ; if (i > begin && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1 ]) continue ; path.addLast(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates, i + 1 , len, target - candidates[i], path, result); path.removeLast(); } } }
Python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution : def __init__ (self ): self.path = [] self.results = [] def combinationSum2 (self, candidates: list , target: int ) -> list : arr_len = len (candidates) if arr_len == 0 : return self.results candidates.sort() self.dfs(candidates, 0 , arr_len, target) return self.results def dfs (self, candidates: list , begin: int , arr_len: int , target: int ) -> None : if target == 0 : self.results.append(self.path[:]) return for i in range (begin, arr_len): if target - candidates[i] < 0 : break if i > begin and candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1 ]: continue self.path.append(candidates[i]) self.dfs(candidates, i + 1 , arr_len, target - candidates[i]) self.path.pop()
Go 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 func combinationSum2 (candidates []int , target int ) int { arrLen := len (candidates) var results [][]int if arrLen == 0 { return results } var path []int sort.Ints(candidates) dfs(candidates, 0 , arrLen, target, &results, path) return results } func dfs (candidates []int , begin, arrLen, target int , results *[][]int , path []int ) if target == 0 { *results = append (*results, append ([]int {}, path...)) return } for i := begin; i < arrLen; i++ { if target < candidates[i] { break } if i > begin && candidates[i] == candidates[i-1 ] { continue } path = append (path, candidates[i]) dfs(candidates, i+1 , arrLen, target-candidates[i], results, path) path = path[:len (path)-1 ] } }