在图论中,由一个有向无环图的顶点组成的序列,当且仅当满足下列条件时,才能称为该图的一个拓扑排序 (Topological sorting):
序列中包含每个顶点,且每个顶点只出现一次;
若A在序列中排在B的前面,则在图中不存在从B到A的路径。
适用范围:
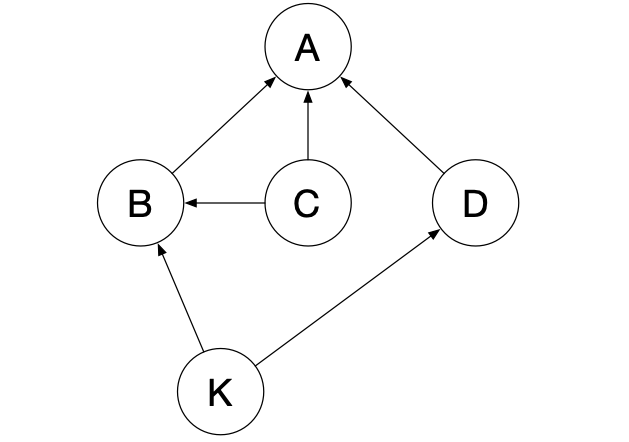
拓扑排序常应用于有依赖关系的一组事务之间的排序. 例如有依赖关系的多个模块的编译次序问题等. 假定下图中的 A , B , C , D , K 为待编译的几个模块, 箭头表示依赖关系(如 B , D 依赖于 K ), 经拓扑排序后应输出模块编译顺序, 即 K -> C -> B -> D -> A 或 C -> K -> B -> D -> A ( K 和 C , B 和 D 顺序可互换)
思路 先找到所有入度为 0 的节点并输出, 删除这些节点. 在下一次迭代中, 找到剩余节点中入度为 0 的节点并输出, 直到图中节点全部输出为止.
Java 图的结构定义及实现见另一篇博客
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class TopologySort { public static List<GraphNode> topologySort (Graph graph) { HashMap<GraphNode, Integer> inMap = new HashMap <>(); Queue<GraphNode> zeroInQueue = new LinkedList <>(); for (GraphNode node : graph.nodes.values()) { inMap.put(node, node.in); if (node.in == 0 ) zeroInQueue.add(node); } List<GraphNode> result = new ArrayList <>(); while (!zeroInQueue.isEmpty()) { GraphNode cur = zeroInQueue.poll(); result.add(cur); for (GraphNode next : cur.nexts) { inMap.put(next, inMap.get(next) - 1 ); if (inMap.get(next) == 0 ) { zeroInQueue.add(next); } } } return result; } }
Python 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 def topology_sort (graph ): in_dict = dict () zero_in_list = [] for node in graph.nodes.values(): in_dict[node] = node.in_degree if node.in_degree == 0 : zero_in_list.append(node) result = [] while zero_in_list: cur = zero_in_list.pop() result.append(cur) for next in cur.nexts: in_dict[next ] = in_dict[next ] - 1 if in_dict[next ] == 0 : zero_in_list.append(next ) return result