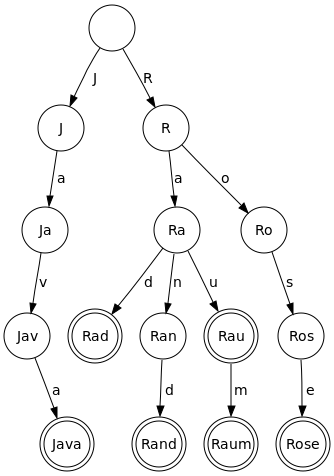
前缀树 又称 字典树, 是一种有序多叉树结构. 常用于做词频统计和前缀匹配. 与二叉树结构不同, 数据不保存在节点中, 而是由路径来表示. 节点中存储标记信息 (当前节点是否为某一单词的结尾、下一可能的字符等). 如下图中所示, 表示了关键字集合 {“Java”, “Rad”, “Rand”, “Rau”, “Raum”, “Rose”}。
实现 Trie (前缀树)
Trie(发音类似 “try”)或者说 前缀树 是一种树形数据结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串数据集中的键。这一数据结构有相当多的应用情景,例如自动补完和拼写检查。
请你实现 Trie 类:
Trie() 初始化前缀树对象。void insert(String word) 向前缀树中插入字符串 word 。boolean search(String word) 如果字符串 word 在前缀树中,返回 true(即,在检索之前已经插入);否则,返回 false 。boolean startsWith(String prefix) 如果之前已经插入的字符串 word 的前缀之一为 prefix ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例:
输入
[“Trie”, “insert”, “search”, “search”, “startsWith”, “insert”, “search”]
[[], [“apple”], [“apple”], [“app”], [“app”], [“app”], [“app”]]
输出
[null, null, true, false, true, null, true]
解释
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple");
trie.search("app");
trie.startsWith("app");
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app");
|
提示:
1 <= word.length, prefix.length <= 2000word 和 prefix 仅由小写英文字母组成insert、search 和 startsWith 调用次数 总计 不超过 3 * 104 次
题解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| class TrieNode {
boolean isEnd;
TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26];
}
class Trie {
private final TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
this.root = new TrieNode();
}
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int nextIdx = c - 'a';
if (cur.children[nextIdx] == null) {
cur.children[nextIdx] = new TrieNode();
}
cur = cur.children[nextIdx];
}
cur.isEnd = true;
}
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int nextIdx = c - 'a';
if (cur.children[nextIdx] == null) return false;
cur = cur.children[nextIdx];
}
return cur.isEnd;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (char c : prefix.toCharArray()) {
int nextIdx = c - 'a';
if (cur.children[nextIdx] == null) return false;
cur = cur.children[nextIdx];
}
return true;
}
}
|
单词搜索 II
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个单词(字符串)列表 words, 返回所有二维网格上的单词 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过 相邻的单元格 内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母在一个单词中不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
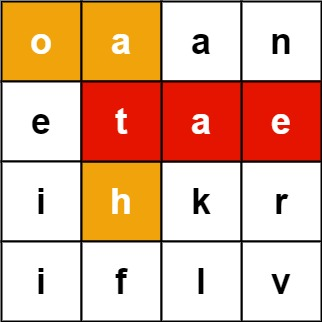
输入:board = [[“o”,”a”,”a”,”n”],[“e”,”t”,”a”,”e”],[“i”,”h”,”k”,”r”],[“i”,”f”,”l”,”v”]], words = [“oath”,”pea”,”eat”,”rain”]
输出:[“eat”,”oath”]
示例 2:
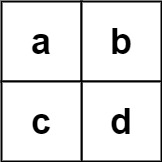
输入:board = [[“a”,”b”],[“c”,”d”]], words = [“abcb”]
输出:[]
提示:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j] 是一个小写英文字母- 1 <= words.length <= 3 * 104
- 1 <= words[i].length <= 10
words[i] 由小写英文字母组成words 中的所有字符串互不相同
题解
可使用前缀树优化 words 中单词的搜索过程,以下解法中前缀树节点直接保存了以当前字母为结尾的单词,以省去添加符合条件的字符串时的二次遍历。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| class TrieNode {
String s;
TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26];
public void insert(String s, TrieNode cur) {
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
int nextIdx = c - 'a';
if (cur.children[nextIdx] == null) {
cur.children[nextIdx] = new TrieNode();
}
cur = cur.children[nextIdx];
}
cur.s = s;
}
}
class Solution {
private Set<String> result;
private char[][] board;
private boolean[][] visited;
private int m, n;
private int[][] directions = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
result = new HashSet<>();
this.board = board;
visited = new boolean[m][n];
TrieNode root = new TrieNode();
for (String word : words) root.insert(word, root);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int cur = board[i][j] - 'a';
if (root.children[cur] != null) dfs(i, j, root.children[cur]);
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(result);
}
private void dfs(int i, int j, TrieNode node) {
if (node.s != null && node.s.length() > 10) return;
if (node.s != null) result.add(node.s);
visited[i][j] = true;
for (int[] direction : directions) {
int newI = i + direction[0], newJ = j + direction[1];
if (newI < 0 || newI >= m || newJ < 0 || newJ >= n || visited[newI][newJ]) continue;
int nextIdx = board[newI][newJ] - 'a';
if (node.children[nextIdx] != null) {
dfs(newI, newJ, node.children[nextIdx]);
}
}
visited[i][j] = false;
}
}
|


