题目
给定两个单链表的头结点 head1 和 head2 , 这两个链表可能有环也可能无环, 请判断这两个链表是否相交, 若相交则返回第一个相交结点
要求
如果链表的长度分别为 M 和 N , 时间复杂度为 O(M+N) , 额外空间复杂度为 O(1)
题解
可采用先将一个链表中的结点放入 HashSet 中, 再遍历另一个链表判断结点是否已在该 HashSet 中的方法, 但额外空间复杂度不符合条件.
不使用 HashSet 的解法:
若链表无环
此时若两链表相交则至少共用两链表的最后一个结点, 只需判断两链表的最后一个结点是否相同即可. 若要找到第一个相交结点需先统计链表长度
L1和L2, 较长的链表的指针先移动abs(L1-L2)步, 剩余的部分即与较短的链表长度相同, 再同时移动相同步数后即可找到第一个相交结点.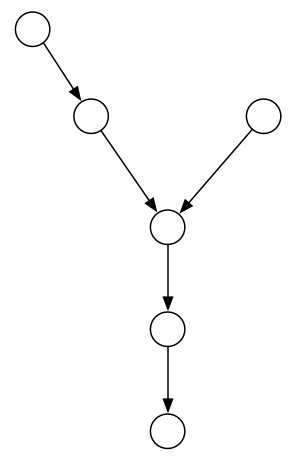
若一个链表有环一个无环
此时对两个单链表来说二者不可能相交
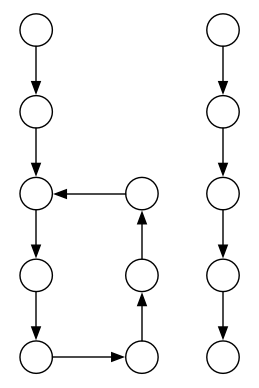
若两个链表都有环
此时有三种情况
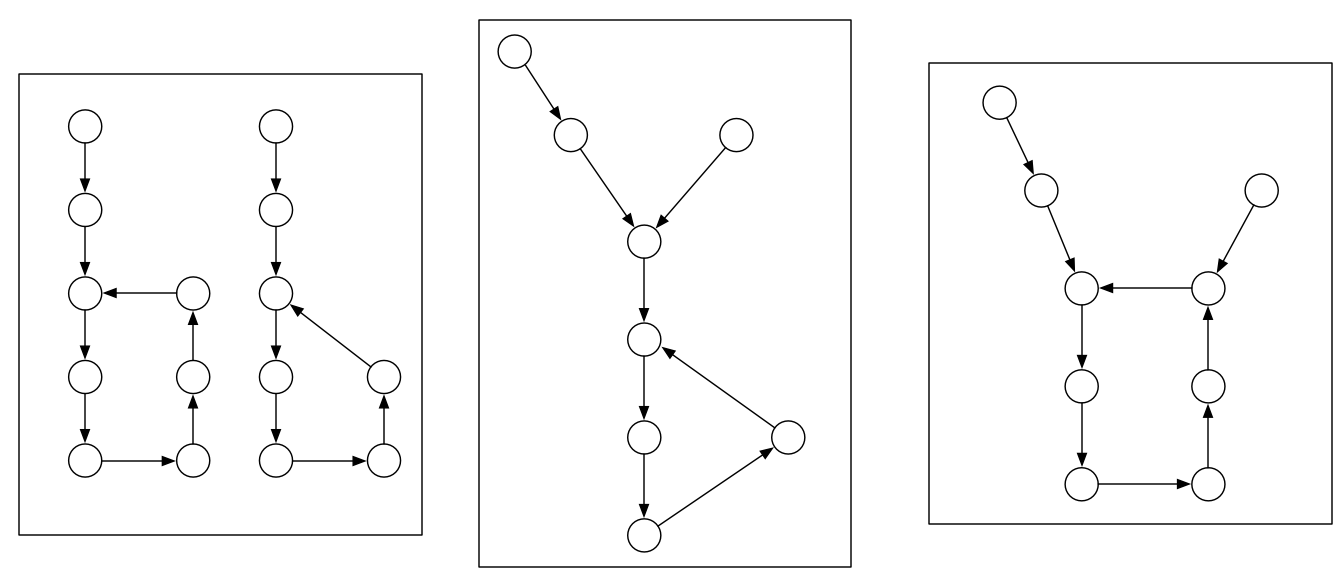
- 若两个链表的入环结点相同, 则为图2
- 若另两个链表的入环结点不同, 则可能有图 1 和图 3 两种可能. 可从一个入环结点开始继续遍历, 若再次遍历回该结点之前经过了另一个入环结点则为图 3 情况, 否则为图 1 情况, 即二者不相交.
Java
1 | class ListNode { |
Python
1 | class ListNode: |
例题 LeetCode # 160
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
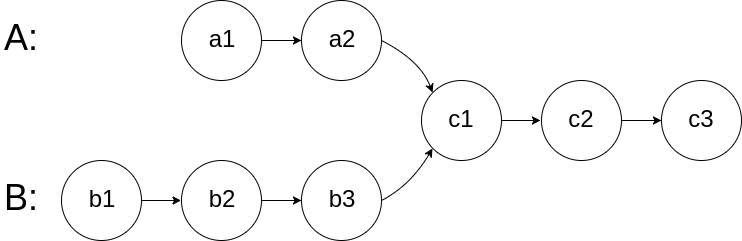
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
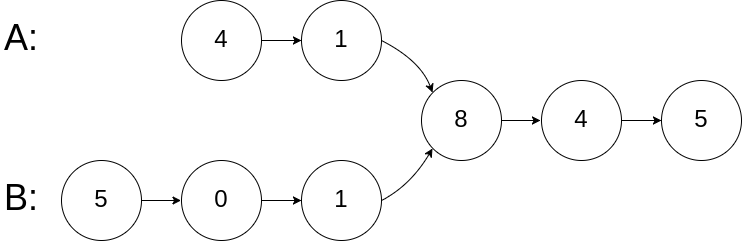
1 | 输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 |
示例 2:
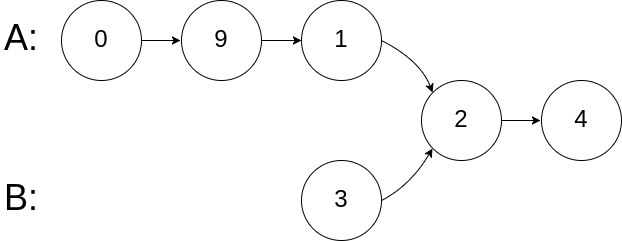
1 | 输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 |
示例 3:
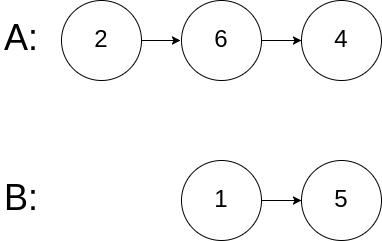
1 | 输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 |
注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
- 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
Java
1 | class ListNode { |
Python
1 | class ListNode: |